What are bile duct stones?
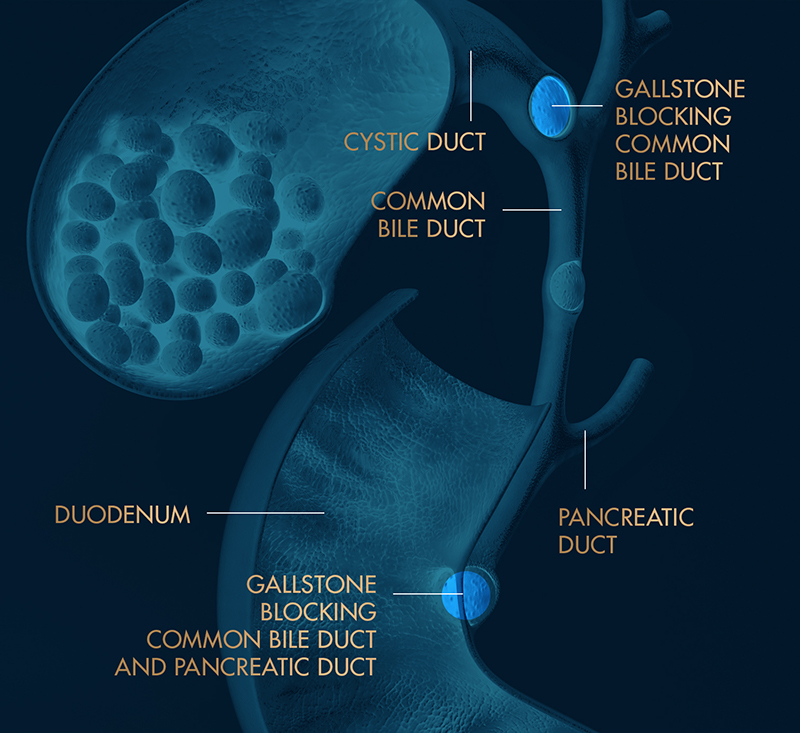
Bile is a golden-yellow fluid produced by the liver which helps in the digestion of fats in our diet (it is also why our stools are brown-yellowish). Bile travels through tiny tubes called Bile ducts from the liver to the small intestine (duodenum). Some of the bile produced is stored in the gallbladder.
Sometimes, stones which form in the gallbladder (gallstones) may drop into the bile duct, causing blockage and resulting in jaundice (yellowing discolouration of the eyes and tea-coloured urine and pale stools).
How do bile duct stones develop?
Most of the bile duct stones originate from the gallbladder as gallstones when there is an imbalance of the bile and it becomes too concentrated in the gallbladder. However, bile duct stones can develop anywhere in the biliary tract where there is bile - within the liver, gallbladder and common bile duct.
Most gallstones do not cause symptoms, but they can be squeezed out of the gallbladder into the bile ducts(choledocholithiasis) and cause problems if they block the bile duct or the pancreas.
Risk Factors
Generally similar to risk factors for gallstones, any disease that results in a slow flow of bile or imbalance of the bile constituents
- Age of 40 years or older
- Females
- Pregnancy
- Family history of gallstones or bile duct stones
- Obesity / Overweight
- High-fat diet / Sedentary lifestyle
- Diabetes mellitus
- Drugs- Cholesterol -lowering medications, birth control pills
- Congenital or acquired abnormalities of bile ducts
- Bacterial or parasitic infections of the bile duct- e.g., Recurrent pyogenic cholangitis (RPC)
- Others - Certain blood disorders - e.g., Hemolytic anemias, liver cirrhosis, prolonged intravenous feeding
Symptoms of bile duct stones
Bile duct stones can cause pain in the upper abdomen, which is felt most often after a meal. If the stone causes blockage of the bile duct, it can also cause the following symptoms:
- Jaundice - Yellowing of the skin and eyes, pale stools, tea-coloured urine
- Fever, Chills or Rigors
- Loss of appetite and weight
- Nausea and vomiting
- Severe, persistent abdominal pain
Diagnosis
When bile duct stones are suspected, after a comprehensive review and examination, the doctor may order some blood tests and imaging tests to visualise the gallbladder and bile duct. These include liver function tests, an ultrasound, computerised tomography (CT) scan, and/or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI/MRCP).
Bile duct stones can potentially result in serious problems if the obstruction is acute and/or prolonged resulting in severe infection (Cholangitis or Sepsis), inflammation (acute pancreatitis) or liver dysfunction or failure.
Do consult a specialist early for an assessment and treatment should you be experiencing any discomfort in your abdomen or any of the symptoms listed above.